|
|
|||||||||||
| Diese Seite auf Deutsch | Multi-celled animals (Metazoa) |
||||||||||
BONY FISHES |
CHORDATA (VERTEBRATES)
|
||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Scorpionfishes Scorpionfishes and Lionfishes Stonefish Leaffish or leaf scorpionfish Stingfishes and Devilfishes
|
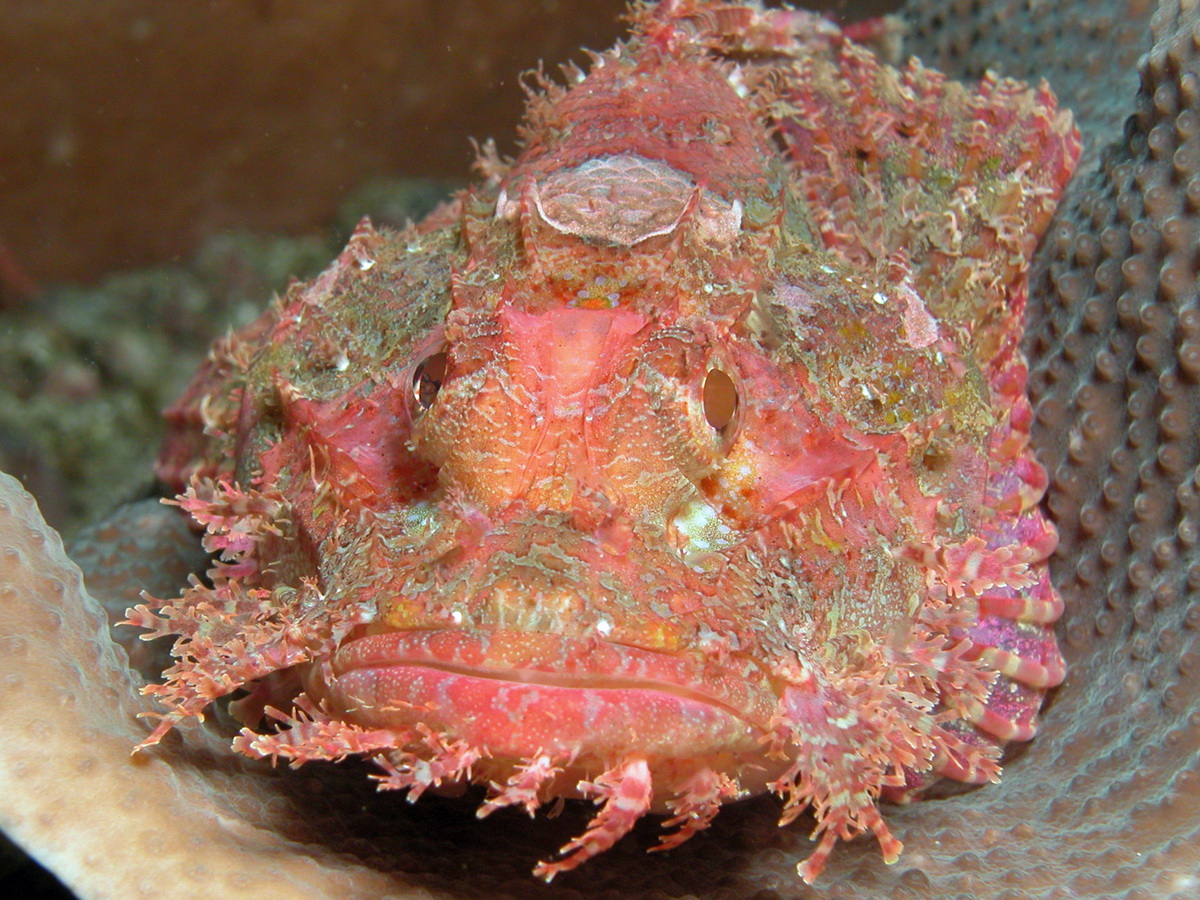
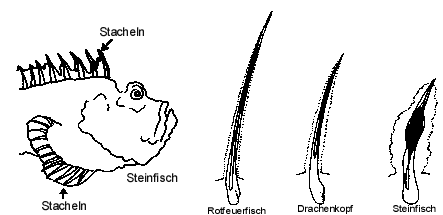
The family Scorpaenidae contains around 45 genera and 380 species. CharacteristicsScorpionfishes have large, heavily ridged and spined heads. Venomous spines on their back and fins with a groove and venom sack. Well camouflaged with tassels, warts and colored specks. Some scorpionfishes can change their color to better match their surroundings. The stonefish is a master of disguise and deception, it looks like a piece of coral or sand covered rock. Thus he can blend in with its surroundings and go unnoticed by its prey. Ecology and rangeMost scorpion fishes live on or near the bottom. They lie in crevices, in caves and under overhangs. Range: Red Sea , pacific ocean to Australia, Hawaii. A few scorpionfishes (no lionfishes or stonefishes) live in the Caribbean. BehaviorThey feed on crustaceans, cephalopods and fishes employing a lie-in-wait strategy, remaining stationary and snapping prey that comes near. With their mouth they create a vacuum and suck prey in during a nearly imperceptible split-second movement (15 milliseconds). Some have algae and hydroid growth on their body surfaces( stonefish) and at least one species (Decoy scorpionfish Iracundus signifier) has a dorsal fin that looks like a swimming fish, a behavior similar to that of the frogfish. Some species (for example the weed scorpionfish) sway their bodies from side to side so they look like a piece of debris. Scorpionfishes are not aggressive, but if threatened they will erect their dorsal spines. If danger continues they flee, usually very fast but only for a short distance and then quickly settle back and freeze. The stonefishes for example ususally bury themselves in sand or rubble using a shoveling motion of their pectoral fins. In a matter of less than 10 seconds only the dorsal portion of the head remains exposed, some sand is thrown on top to further enhancing concealment. Some species like the devilfish have very bright red and yellow colors on the inner surface of their pectoral fins. Those colors are not visible when resting but are flashed if threatened. Scorpion fishes produce a floating, gelatinous mass in which the eggs are embedded. |
||||||||||
|
spines lionfish scorpionfish stonefish |
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
Scorpionfishes have a reddish to brownish color and are mottled. This enables them to disappear against the substrate. Scorpaenopsis
|
|||||||||||
| The stonefish is extremely difficult to see because it usually buries most of its body under sand or rubble and only their widely separated eyes show. Often algae and hydroids grow on its back. It has been suggested, that stonfishes exude a white, milky substance over their bodies which encourages plant growth. Shrimps and other animals have been observed to climb over them. This is the worlds most venomous fish. Their near perfect camouflage and the venomous spines make them a hazard for swimmers, snorkelers and divers in shallow water. Wounds should be treated immediately with hot water or dry heat. There is a scorpionfish that erroneously identified as stonefish, the humpbacked or devil scorpionfish. However there are two difference: First the shape of the mouth. Stonefishes have a mouth which is directed upwards like a upside-down "U". Second the stone fish curl their tail extremely to one side.
|
|||||||||||
The leaffish has a thin leaf-like body. Several color varieties exist (red, yellow, white, pink, black). It rocks from side to side to mimic a piece of debris in a current. They regularly occur in pairs and usually don't move much around, so they can be found again on several dives.
|
|||||||||||
| Lionfishes are boldly colored in red, white and black. This coloring however fades in low-light conditions such as dusk and then the stripes serve as disruptive camouflage. With their long fin spines they resemble crinoids (featherstars) which helps them to masquerade, when selecting a ambush site. Lionfishes have been observed to hunt in a pack, rounding up small fish. When they approach their prey, they spread their fins to the side and slightly forward. The fins act as a barrier to cut off the escape of the prey.
|
|||||||||||
| Devilfishes (also called sea goblins, bearded ghouls and demon stingers) have very special pectoral fin rays that can be moved independently from the rest of the fin. This looks as if the devilfish was walking over the ground. They look very clumsy and unwieldy because they also drag their extremely curved tails. The inner surface of their pectoral fins are brightly colored and they flash them if threatened. Sometimes several fish lie together. Devilfishes occur on sand and mud bottoms close to reefs and in seagrass meadows. They often bury themselves in the substrate.
|
|||||||||||
Rhinopias |
Rhinopias scorpionfishes are extremly well camouflaged und thus rarely found. They live mostly on rubble, sand and small coral reefs. There are 8 species of Rhinopias, most of them only live in a small area: Rhinopias argoliba - endemic to Japan (Sagami Bay) / Rhinopias filamentosus - only known from the Philippines / Rhinopias xenops (strange-eyed scorpionfish) - only known from Hawaii and Japan / Rhinopias cea - endemic to the Easter islands / Rhinopias godfreyi (Godfrey's scorpionfish) known only from West-Australia and Papua New Guinea. The 3 better known species and the relevent differences: Attention: My personal opionion is, contrary to the scientific papers, that Rhinopias frondosa and Rhinopias eschmeyeri are a morphological variations of the same species, one variation with more and one with less tentacles. See separate page only about Rhinopias. |
||||||||||
Photos of scorpionfishes (scorpionfishes / unusual scorpionfishes) click for enlargement
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Waspfishes (Tetrarogidae)This family don't belong to the family of scorpionfishes but waspfishes look very similar to some of them, specially to the leaffish (some ichtyologists place them in the family of scorpionfishes, some don't). The family of waspfishes contains about 11 genera, like Ablabys, Paracentropogon and Richardsonichthys. The dorsal fin of the waspfishes originates above the eyes. They are laterally compressed and look like a leaf. Most of these waspfishes occur on or near coastal reefs. |
||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
Velvetfishes (Aploactinidae)This family is not very known. Velvetfishes are elongate and compressed. Bony knobs rather than spines on head, thick fins. Loose, wrinkly looking skin, some like sandpaper. Most live in temperate waters around Australia, some occur on sand or rubble. 17 genera, 25 species. |
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
Photos of waspfishes and velvetfishes click for enlargement
|
|||||||||||
index - Coral reefs - The ocean - Reefs at risk - Major endangered reef regions (hotspots) - photo collection - the stonefish page - starfish site mapLINKS ABOUT FISHES |
|||||||||||
. Copyright Teresa Zubi